Smart Placement
By default, Workers and Pages Functions execute in the data center that receives the request. If your Worker relies on back-end resources (like a database), running closer to that backend—not necessarily to the end user—can be faster. Smart Placement automatically runs your workload in the best location to minimize latency.
Background
Consider how proximity to your backend changes latency:
Suppose a user in Sydney, Australia hits a Workers app that must call a database in Frankfurt, Germany multiple times per request.
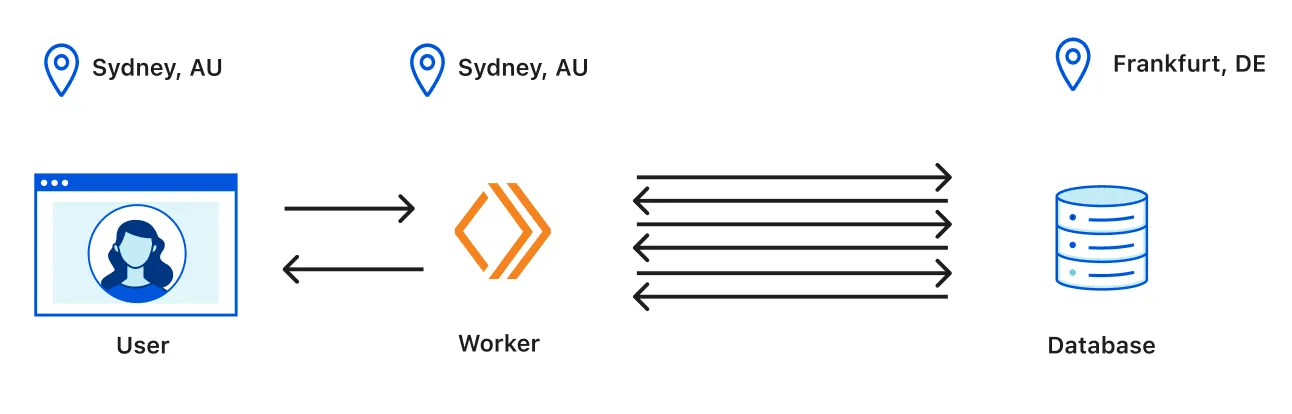
The bottleneck is all the round trips to the database. With Smart Placement, Cloudflare runs the Worker near the database instead of near the user.
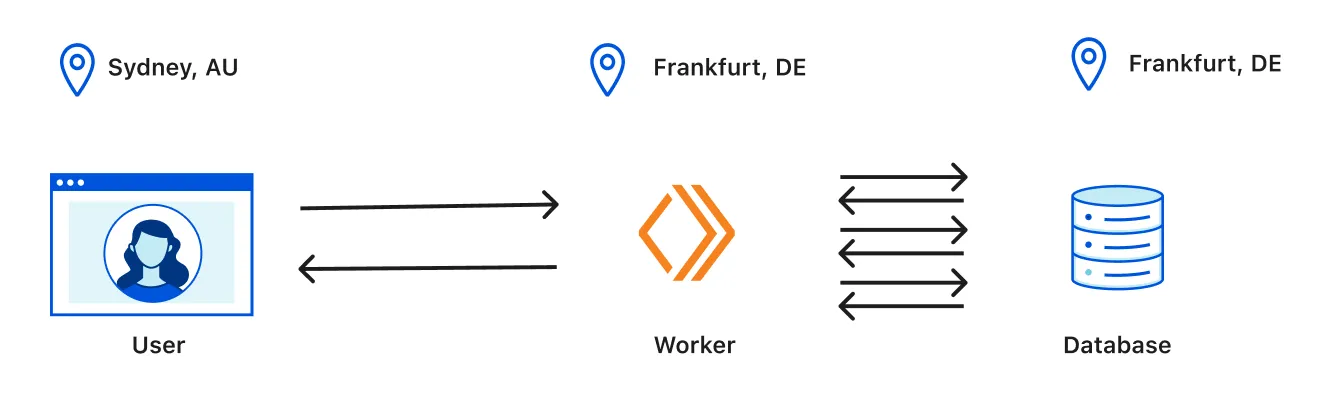
How Smart Placement works
Smart Placement is enabled per Worker. After you turn it on, Cloudflare periodically analyzes request duration across candidate locations. It compares the estimated duration at the receive location (default execution) versus other locations, factoring both execution speed and added network latency to forward the request. If a candidate is significantly faster, the request is routed there; otherwise it runs at the nearest default location.
Smart Placement only considers locations where the Worker has previously run, because estimates rely on historical data. It won’t place a Worker in a region that has seen no traffic.
It only affects the fetch handler. RPC methods or named entrypoints are unaffected. Workers without a fetch handler are ignored; Workers with both fetch and other handlers see Smart Placement applied only to fetch.
Static assets are also unaffected: they’re still served from the edge closest to the incoming request. If your Worker fetches assets via a static asset binding, those assets come from wherever the Worker is running.
Enable Smart Placement
Available to all Workers plans.
Enable via Wrangler
Install
wrangler@2.20.0or newer (guide).Add to your Wrangler config:
wrangler.jsonc
{ "$schema": "./node_modules/wrangler/config-schema.json", "placement": { "mode": "smart" } }wrangler.toml
[placement] mode = "smart"Wait for analysis (up to ~15 minutes).
Review request duration analytics.
Enable via Dashboard
- In the Cloudflare Dashboard, open Workers & Pages.
Go to Workers & Pages - In Overview, select your Worker.
- Choose Settings > General.
- Under Deployment locations, choose Smart.
- Wait for analysis (needs sustained traffic from multiple regions; up to ~15 minutes).
- Review request duration analytics.
Observability
Deployment status
Worker metadata includes deployment status. Query via:
curl -X GET https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/{ACCOUNT_ID}/workers/services/{WORKER_NAME} \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <TOKEN>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" | jq .
Statuses:
- (none): Not analyzed; runs at the default closest location.
SUCCESS: Analyzed and optimized; runs wherever estimated request duration is lowest (could be default or elsewhere).INSUFFICIENT_INVOCATIONS: Not enough traffic yet; runs at the default closest location.UNSUPPORTED_APPLICATION: Smart Placement tried and made it slower; reverted to default and won’t re-analyze until redeploy. Rare (<1%).
Request duration analysis
After enabling, duration is measured at the data center closest to the end user.
By default, 1% of requests bypass Smart Placement to serve as a baseline.
cf-placement header
When enabled, Cloudflare adds a cf-placement header so you can see whether a request was routed and where it ran (airport code).
For example: cf-placement: remote-LHR means it was routed to a London-area DC; cf-placement: local-EWR means it ran at the nearest default DC near Newark (EWR).
Beta note: The cf-placement header may be removed before GA.
Best practices
For full-stack apps, split front-end and back-end logic into separate Workers and connect them with Service Bindings.
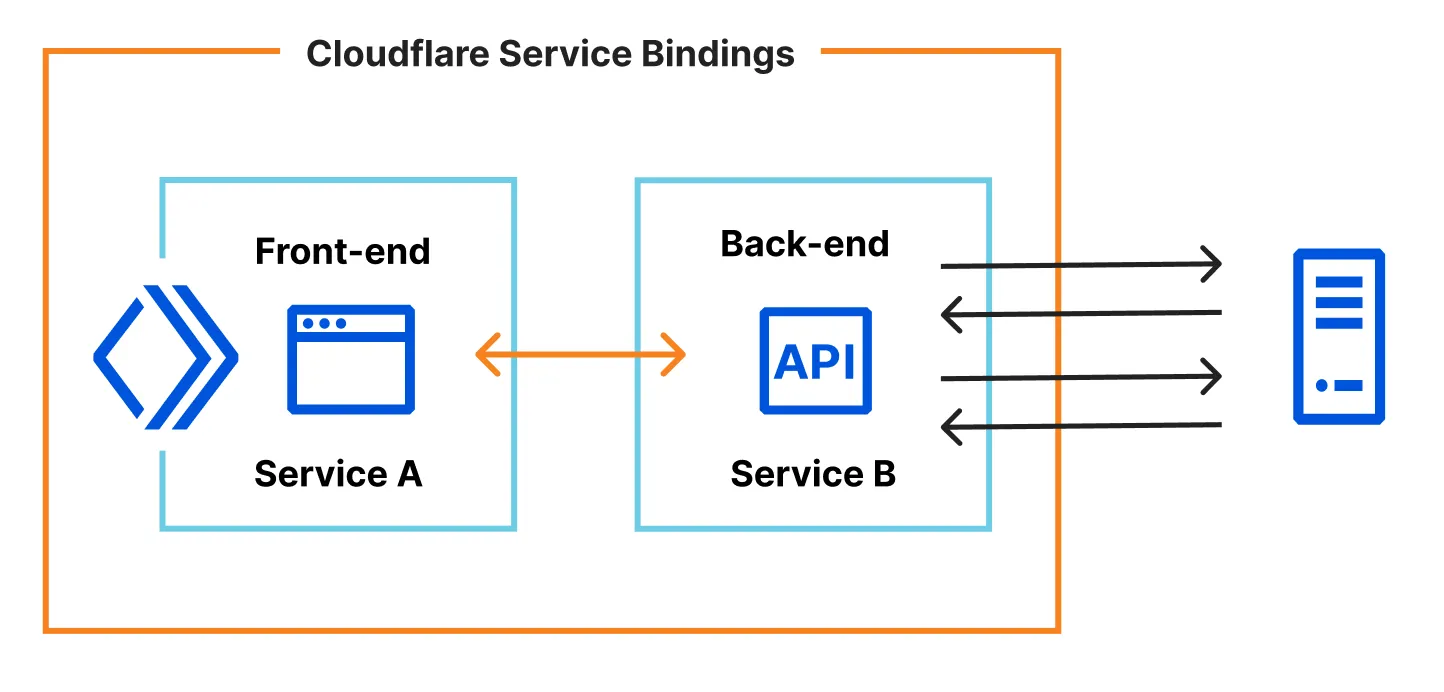
Enable Smart Placement on the back-end Worker so it runs near your data sources, while the front-end Worker stays close to users. You keep a snappy UI and reduce backend round trips.
Summary
Smart Placement automatically chooses where a Worker should run to minimize latency—especially helpful for Workers that frequently call databases or other backends.
Key points
- Automatic optimization: Smart Placement analyzes and selects the best execution region.
- Lower latency: Run closer to backends to cut round trips.
- Easy to enable: Wrangler or Dashboard.
- Observability: Deployment status and duration analytics.
- Architecture tip: Split front-end/back-end Workers; enable Smart Placement on the backend.
Where it helps
- Workers that frequently hit databases
- Workers calling back-end APIs
- Back-end Workers in full-stack setups
- Latency-sensitive workloads
Notes
- Applies only to the fetch handler
- Needs sustained traffic from multiple regions for decisions
- Analysis can take up to ~15 minutes
- Static asset serving locations are unaffected
